5-SECOND SUMMARY:
- Agile methodology is a “step by step” dynamic focused on short-term visibility but never losing the long-term product goal.
- There are 5 main Agile methodologies: Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP), Lean Development e Crystal.
What are agile methodologies?
The first we heard about Agile development (or the term Agile) was back in 2001 when a community of developers that had grown tired of using development methods considered to be “heavy” – namely, the waterfall model – decided to set out a manifesto: The Agile Manifesto. This very important document had so much impact that it has worked as a bible for Agile development even until today, laying out all principles and good practices.
Agile methodologies argue that, above all, we should seek client satisfaction through the continuous delivery of value-adding software, by staying in constant communication with the client, and also by focusing on communication between team members. Contrary to previous practices, Agile methodology is not characterised by the complete definition of a product, but rather “step by step” – a complete analysis or the definition of all categories/requirements, by dynamic interaction that allows constant delivery – Focused on “near-shore” visibility but never losing the long-term product goal.
According to the Agile Manifesto and some of its 12 principles:
?Customer satisfaction is the top priority, demonstrated through continuous delivery and added value.
? Changes to requirements should be accepted – rather than pursuing “rigid” requirements, even if at a late stage in development: “Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage”, as is stated in the Manifesto.
? The customer and the development team should work together on a daily basis, facilitating team and product synchronisation.
? It is vital to provide a pleasant environment and good support to development teams. Only in this way is it possible to keep them motivated.
? Agile processes promote sustainable development due to their constant rhythm and technical excellence, which in turn improves productivity.
? Retrospective moments inside a team are essential, allowing it to make the necessary adjustments and promote efficiency.
Basically, Agile development follows an incremental model, which develops collaboration within the team and continuous planning, as well as everlasting evolution and learning. Agile methodologies should respect the software development cycle – planning, execution and final delivery – therefore allowing software to be developed in stages; this makes it easier to identify and resolve bugs or new needs.
The main advantage of using Agile methodologies is not just the fast delivery of software, but also the constant delivery of “value” to the customer, since deliveries are incremental.
There are countless methodologies that follow this Agile mindset. In this blog post, we highlight the five main Agile methodologies and their advantages and disadvantages in the software development universe. But we cannot dive into the different methodologies without first referring to the growing popularity of the Agile methodologies (or some of them at least) with business management. This proves that is just not software development that can be enriched using these practices.
Business development is becoming an increasingly unpredictable playground, just like software development. So the challenge is now why not implement Agile methodologies in business process management? Agile methods are adaptable, allowing for rapid decision-making and instant influence on business development.
Main Agile methodologies:
1. Scrum
Scrum is, undoubtedly, the most used of the many frameworks underpinning Agile methodology. Scrum is characterised by cycles or stages of development, known as sprints, and by the maximisation of development time for a software product towards a goal, the Product Goal. This Product Goal is a larger value objective, in which sprints bring the scrum team product a step closer.
It is usually used in the management of the development of software products but can be used successfully in a business-related context.
Every day starts with a small 15-minute meeting, the daily Scrum, which takes the role of synchronising activities and finding the best way to plan out the working day, allowing for a check on sprint “health” and product progress.
Advantages:
- Team motivation is good because programmers want to meet the deadline for every sprint;
- Transparency allows the project to be followed by all the members in a team or even throughout the organisation;
- A simple “definition of done” is used for validating requirements
- Focus on quality is a constant with the scrum method, resulting in fewer mistakes;
- The dynamics of this method allow developers to reorganise priorities, ensuring that sprints that have not yet been completed get more attention;
- Good sprint planning is prioritised, so that the whole scrum team understands the “why, what and how” of allocated tasks.
Disadvantages:
- The segmentation of the project and the search for the agility of development can sometimes lead the team to lose track of the project as a whole, focusing on a single part;
- Every developer role may not be well defined, resulting in some confusion amongst team members.
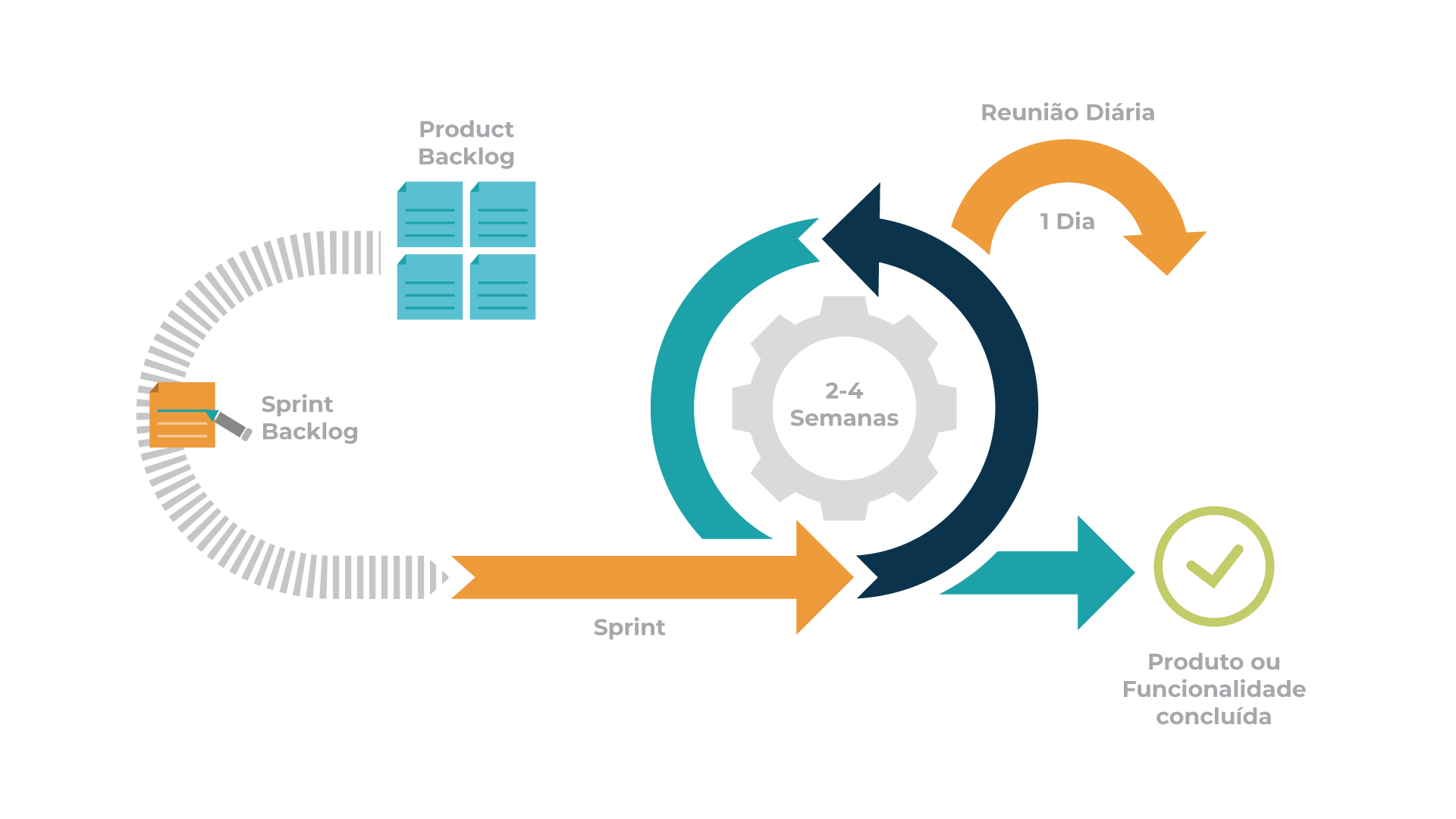
2. Kanban
The word Kanban is of Japanese origin and its meaning is linked to the concept of “just in time”. In practice, the Kanban method is organised on a board or table (Kanban board), divided into columns, showing every flow within the software production project. As the development evolves, the information contained in the table changes, and whenever a new task comes into play, a new “card” is created.
This methodology is also useful in individual business departments, such as HR, marketing, etc., bringing the desired visibility over all the team’s tasks.
The Kanban method requires communication and transparency so that the members of any team all know exactly what stage development is at and can see the status of a project at any time. It primarily focused on team capacity and is best for processes that undergo small changes.
Advantages:
- Ability to view all the tasks under a single project (by Completed, In Progress or In testing, for example) using the simple concept of “Cards”;
- You can limit the number of running tasks (that is, the amount of work, bearing its resolution or deliverability in mind);
- Focuses on the duration of a cycle – how long it takes a task to go from backlog to final stage;
- Allows continuous deliveries;
- Probably one of the simplest methodologies to implement outside the “IT world”.
Disadvantages:
- It’s possible for team members to misinterpret the information shown on the Kanban Board, especially when it is shown as outdated;
- Since there are no timeframes in Kanban, you can face time-related problems, such as delays, at each and every stage.

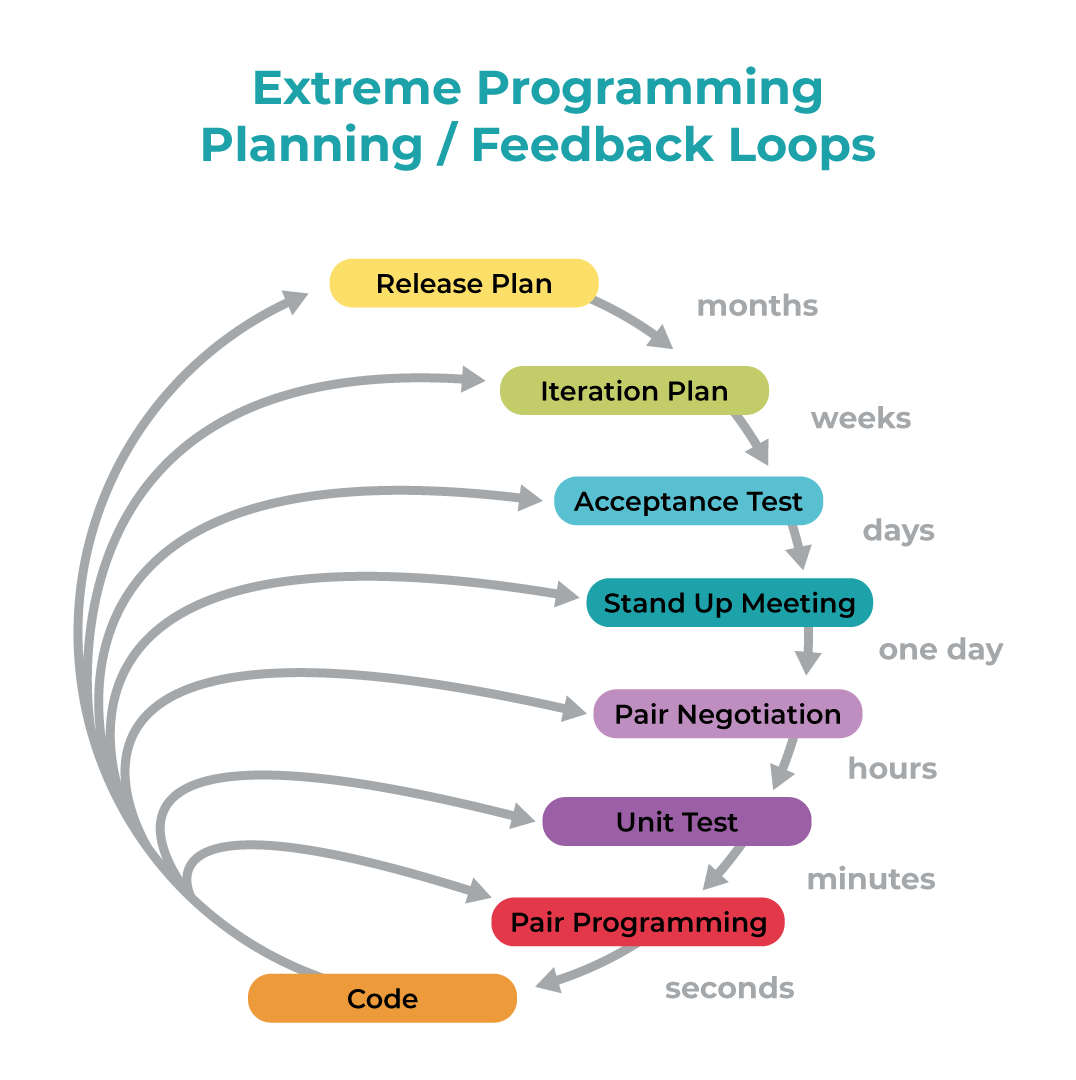
3. Extreme Programming (XP)
This is a typical Agile development framework, developed by Kent Beck, and can be adapted to development companies of various dimensions.
Extreme Programming (“XP”) methodology is based around the idea of discovering “the simplest thing that will work” without putting too much weight on the long-term product view.
It is a methodology that emphasises values such as Communication, Simplicity, Feedback, Courage and Respect, and prioritises customer satisfaction over everything else. This methodology encourages trust by motivating developers to accept changes in customer requirements, even if they arrive during the latter stages of the development cycle.
Teamwork is extremely important in XP, since, when there is a problem, it is solved by the whole team of managers, developers or customers, bringing them together to promote conversation and engagement and break down barriers to communication. They all become essential pieces of the same puzzle, creating a fertile environment for high productivity and efficiency within teams. In Extreme Programming, the software is tested from day one, collecting feedback to improve development. XP promotes activities such as pair programming, and with a strong testing component, it’s an excellent engineering methodology.
Advantages:
- The simplicity of the written code is an advantage since it allows for improvement at any given time;
- The whole process and the XP development cycle is visible, creating goals for developers along with relatively rapid results;
- Software development is more agile than when using other methodologies, due to constant testing;
- Promotes a highly energising way of working;
- XP also contributes to uplifting and maintaining team talent.
Disadvantages:
- The extreme focus on code can lead to less importance being paid to design, meaning that it has to get extra attention later;
- This framework may not work at its best if all the team members are not situated in the same geographical area;
- In XP projects, a registry of possible errors is not always maintained, and this lack of monitoring can lead to similar bugs in the future.
4. Lean Development
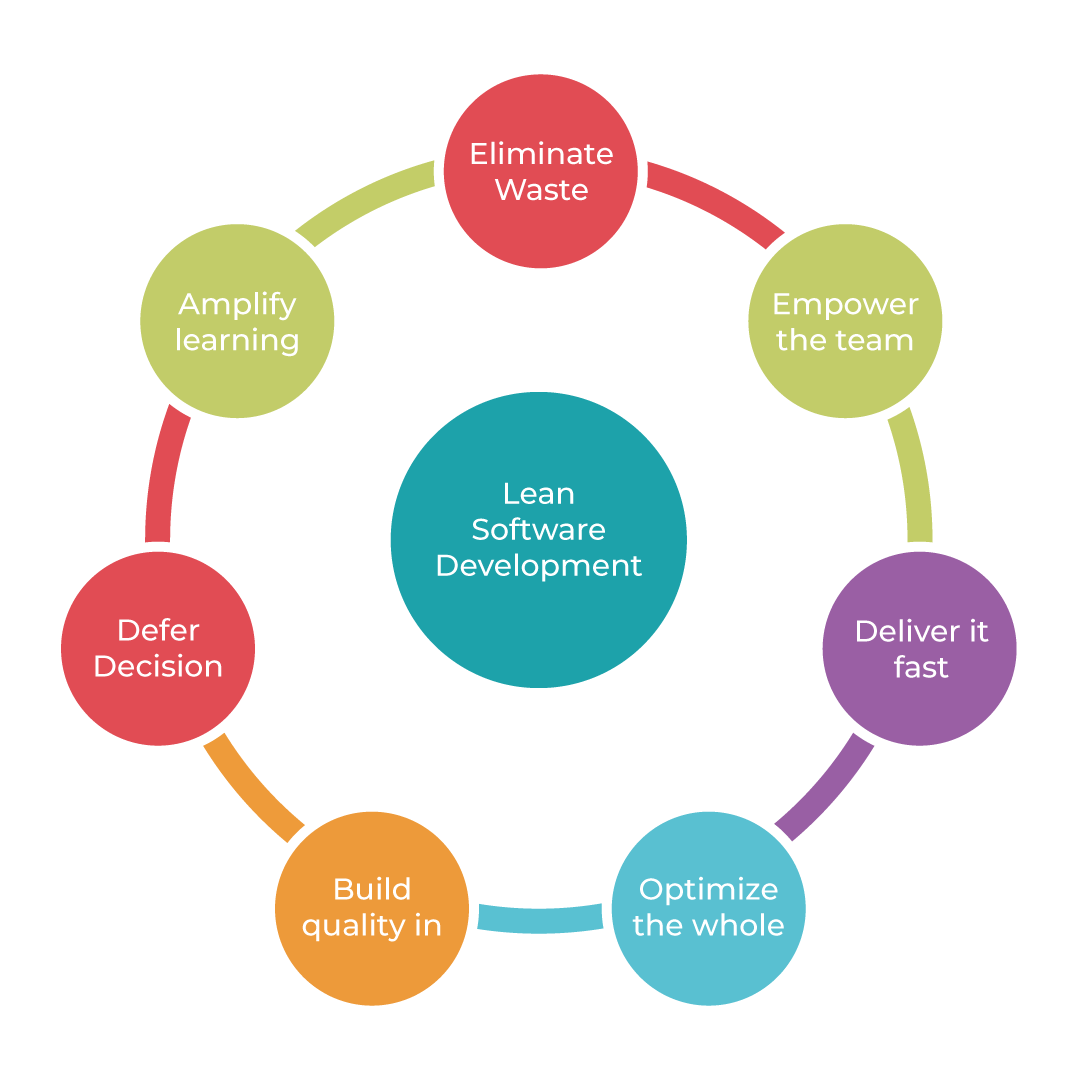
Lean development is a methodology that comes directly from Lean Manufacturing, created by Toyota, and applied to software development. This method offers a conceptual framework and follows values, principles and good development practices that can be applied to an Agile development approach.
Lean development forces the team to ruthlessly remove any activity that does not bring ultimate value to the product.
There are seven essential principles: deleting things that do not matter (anything that does not bring effective value to the customer project); quality development (creating quality in development requires discipline and control of the number of residuals created); creating knowledge (the team is motivated to document the whole infrastructure to later retain that value); differing commitments (this point encourages the team not to focus too much on planning and anticipating ideas without having a complete prior understanding of the requirements of the business); fast delivery (getting value to the customer as soon as possible); respecting the team (communication and managing conflicts are two essential points); optimise the whole (the development sequence has to be perfected enough to be able to delete errors in the code, in order to create a flow of true value).
Works on building simple solutions and presenting them to customers using their feedback on the “product” to incrementally enhance it. The “minimum viable product” concept is also often associated with “Lean”.
Advantages:
- Allows the team to delete superfluous activity, therefore saving time and money;
- Decreases the time needed to deliver functionalities, since it prepares the development team during the decision-making process, hence increasing general motivation;
- Easily scalable methodology, easily adaptable to projects of any dimension;
- Does not over-engineer solutions or business requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Dependent on the development team’s ability and on following “Lean principles”, which requires extremely dedicated and talented developers;
- It is easier to lose focus since various tasks are divided into a number of elements;
- Requires some documents, in particular on the characteristics of the business that is the subject of the work. Otherwise, there is a risk that the development may be carried out incorrectly and present errors.
5. Crystal
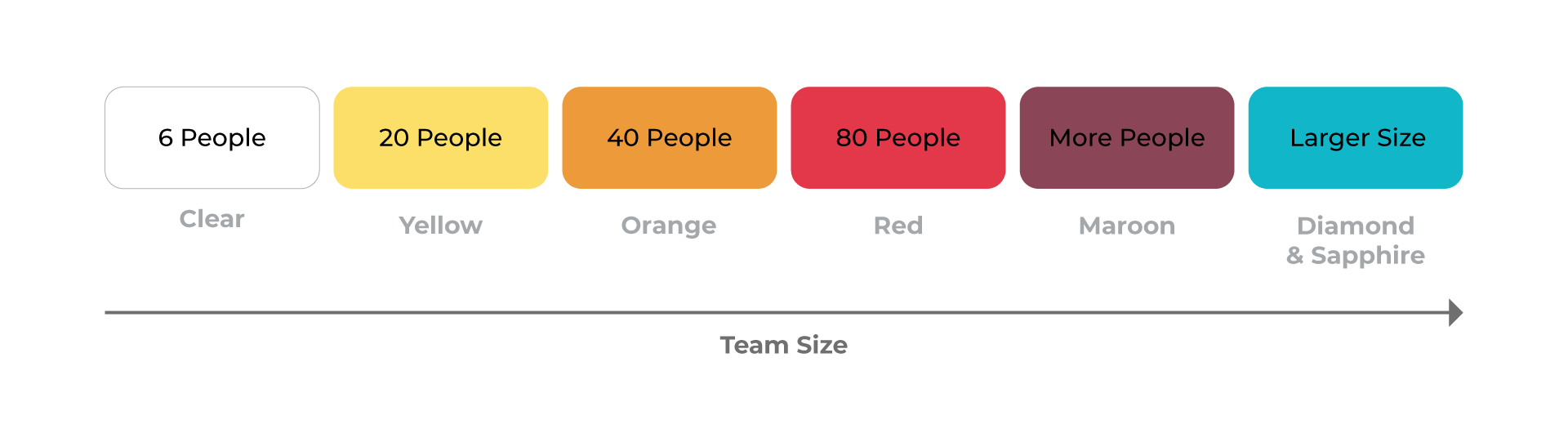
This is a family of Agile methodologies, and Crystal is one of the most flexible frameworks, giving tremendous freedom to the team to develop their own processes. It focuses way more on individuals and how they interact rather than on the process or the tools – so communication is an essential key aspect.
Crystal has variants such as Crystal Clear (up to an 8-person team), Crystal Yellow (up to a 10 to 20-person team), Crystal Orange (up to a 20 to 50-person team) and Crystal Red (for big teams with 50 to 1000 people). Crystal focuses on principles such as People, Interactions, Community, Skills, Talent and Communication, aiming to deliver the best possible software development process. The core of this development process is interaction and symbiosis, which have to exist between the people allocated to the projects and processes in order to bring efficiency to the project.
Each project is unique and undergoes frequent changes, so the team must find their own ways to bring it to its conclusion using the best decisions.
According to its founder, Alistair Cockburn, “Crystal is a family of software development methodologies, which works with the power invested by people, and is extremely light and stretch-to-fit”. Basically, Cockburn believes that talent and the way team members interact brings benefits for the whole project.
It’s a light methodology in terms of documentation, where teams can find their own ways over preferred work modalities, removing management overheads and creating a “free” process.
Advantages:
- Crystal requires frequent deliveries, in order to identify eventual problems at every stage;
- There is always space to improve characteristics, taking some time from software development and allowing for discussions about how to perfect processes;
- Facilitates closer communication within teams and promotes interaction and knowledge-sharing between team members;
- Requires a technical environment with automated tests, configuration management and frequent integration.
Disadvantages:
- The fact that there are variants in the methodology family means that the principles might vary with the size of the team and the size of the project, resulting in projects that might not be so straightforward;
- It might not work best for geographically scattered teams, because of the constant need to communicate and reflect;
- Planning and development are not dependent on requirements;
- It is ideal for experienced, autonomous teams.
Final Thoughts
At Xpand IT, software development is personalised, focusing on results and customer satisfaction, stage by stage. The whole development is governed by Agile principles. Therefore, in order to respect the development cycle, achieve the desired results, predict possible errors, maximise productivity and develop safely, while still keeping team members motivated, we created our own methodology: XPAgile (a mix of Agile frameworks – Scrum and Extreme Programming – that ensures the best results within given deadlines).
For more information on the development methodology of Xpand IT, click here.

Atlassian Project Manager – Xpand IT














