ITIL is an acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, a set of good practices designed to facilitate a significant improvement to the operation and management of all the IT services within a company. When implemented by an organisation, this set of practices becomes an unequivocally beneficial asset, as it comes with several advantages, such as the improvement of risk management, the strengthening of client relationships, an increase in productivity and reduced costs.
Developed in 1980 by the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) – a British government agency – it is the primary framework for sound IT Service Management (ITSM). It began with more than 30 books comprising numerous sources of information, and describing good practices to follow in relation to IT services. Currently, ITIL runs to 5 books covering its various processes and functions (and a total of 26 processes that can be adopted by companies).
In 2005 the framework was finally formally recognised and given the ISO/IEC 20000 Service Management seal of approval for compliance with desired standards, and for being truly aligned with Information Technology best practice.
ITIL went through various revisions and there are now 4 different versions, with the most recent being released at the start of 2019. This updated version maintains a strong focus on automating processes in order to maximise professional time and the business integration of IT departments, in order to improve communication between teams and technical and non-technical staff. Version 4 features new ways to tackle the challenges of modern technology and its main goal is to become ever more agile and cooperative.
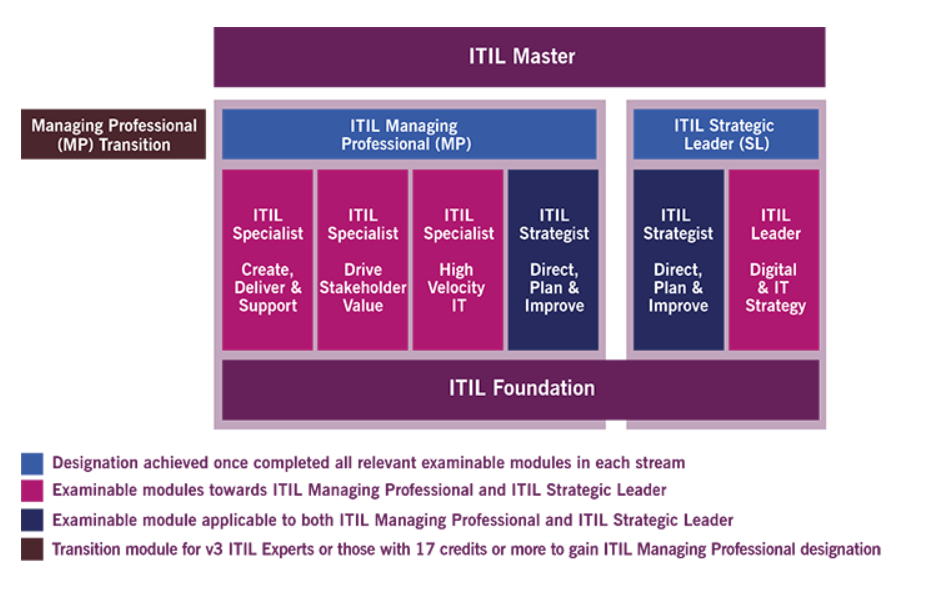
Reading current books on the subject simply won’t give you enough background to effectively implement ITIL for your company, however. You need to engage professionals dedicated specifically to the field, and guarantee adequate training and certifications for both the company and these professionals. Current certification, in accordance with the 4th version of ITIL, is divided into two levels: ITIL Foundation and ITIL Master – each one with its own unique examinations and programme content. There are two options under the ITIL Foundation module: ITIL Managing Professional (which certifies an ITIL specialist), and the ITIL Strategic Leaders certification (encompassing both ITIL Strategist and ITIL Leader certificates). After completing foundation accreditation, you can then leap into master level – the highest certification available in ITIL 4. You can review the full scheme using the table below:
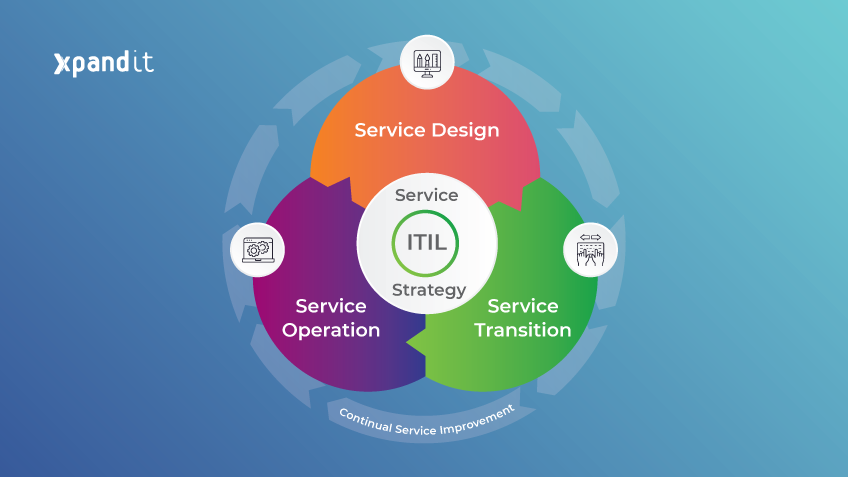
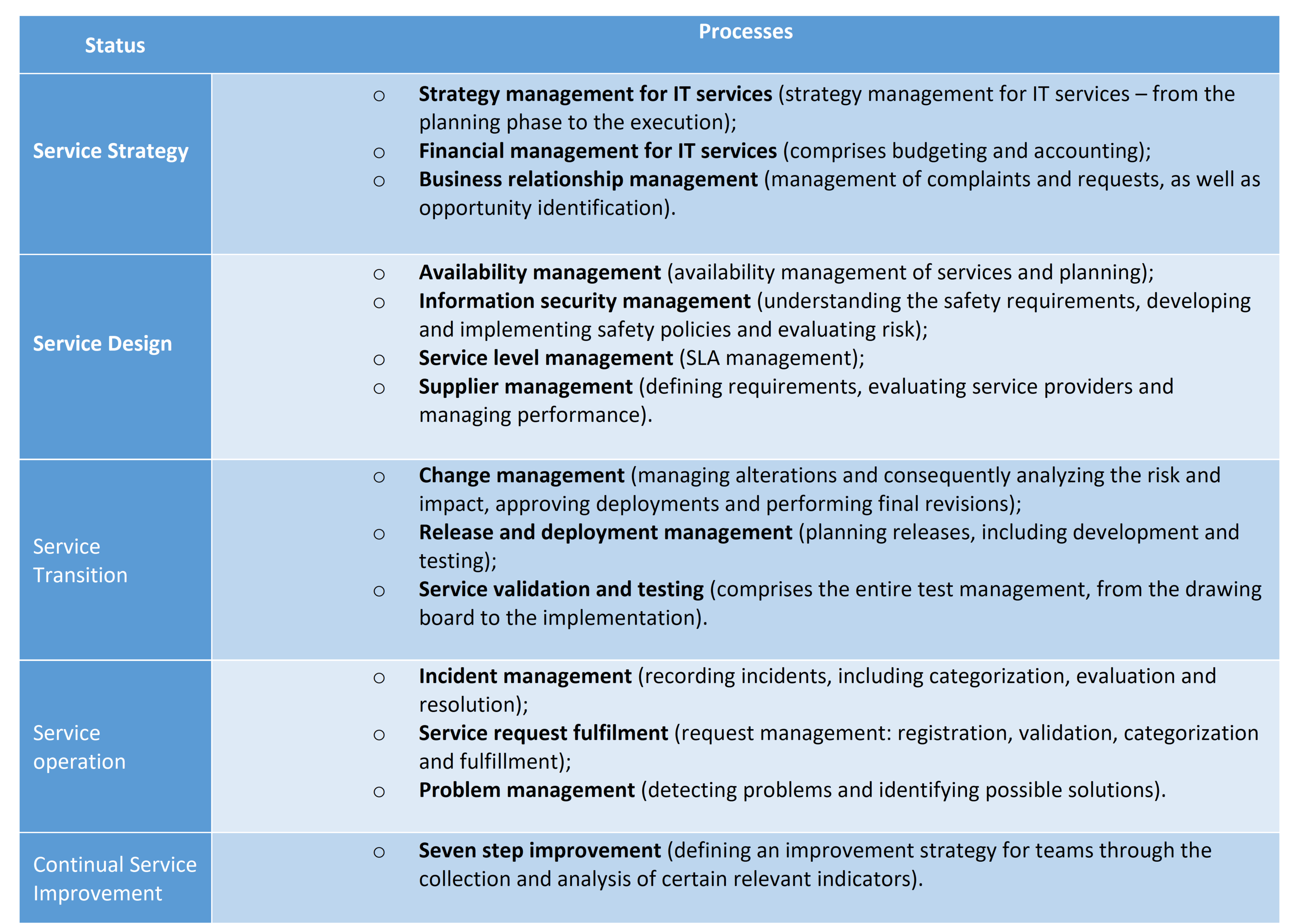
ITIL is divided into five major areas – Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operations and Continual Service Improvement – and each area has individual processes. Although this framework provides 26 processes in total, companies are not obligated to adopt them in their entirety. It is up to the IT professionals and ultimately the CTO to define appropriate procedures to integrate into teams. Below you can find some examples of the most commonly used processes:

Content and Digital Coordinator – Xpand IT