5 SECONDS SUMMARY:
- By applying strategy to UX, we seek a deep understanding of the intersection between business objectives, user needs and implementation capacity.
- But how do we effectively implement this process in a company, respecting its business vision? Find everything in this article.
How often do we come across the promise of a spectacular and innovative digital experience, only to be confronted with the harsh reality of impracticality during deployment?
The idealised concept for the experience gets lost in the technical complexity, resulting in a final product that fails to deliver value and credibility due to the lack of an informed analysis.
It is a common dilemma in the UX universe, overshadowing the original vision and compromising the essence of what makes an effective experience.
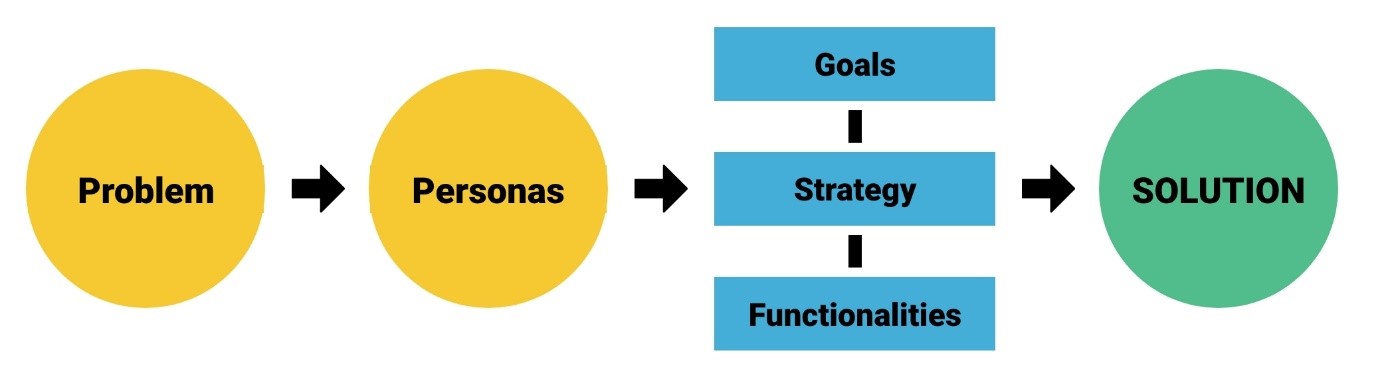
In this challenging scenario, strategy emerges as a key element, filling the gap between project teams. It is the process that unites inspiring vision with pragmatic execution, ensuring that the digital experience is not just an idea but something tangible and impactful.
The concept of strategy resonates in many aspects of everyday life, from sports to corporate decisions. In the context of UX, it is the foundation on which we build memorable digital experiences.
Generally speaking, strategy is the art of planning and directing actions to achieve specific objectives. Whether in business, products or any other area, strategy is the compass that guides the steps towards success.
In UX, this approach is no different.
By applying strategy to UX, we seek a deep understanding of the intersection between business objectives and business vision, user needs and implementation capacity. It is a process of meticulous alignment between a company’s macroeconomic vision and the fundamentals that make the user experience valuable.
1 – Defining a UX strategy
In the world of UX, the strategy must be a robust plan that answers crucial questions:
Dos and don’ts: The UX strategy seeks to outline the actions to be taken and those to be avoided to achieve the proposed results.
What value is being added? It emphasises what makes the product or service unique, providing a clear value proposition that impacts users.
What resources should be made available? It directs where the company’s resources should be focused, ensuring that investment contributes to the overall vision and purpose.
The ultimate goal of the UX strategy is to gain a competitive advantage so you can fulfil your business vision.
It should not be understood as an isolated concept but rather as a mindset present in every decision, every iteration, and every line of code.
2 – The three dimensions of UX strategy
In UX context, the focus of the strategy is threefold:
Business objectives: to align what the company wants to achieve with the digital experience it intends to implement.
Responding to users: putting the user at the centre of the process, understanding their needs, expectations, and pains.
Deployment capacity: ensuring that the ideas expressed in the experience concept can be effectively translated into tangible digital products.
3 – UX strategy as a harmonising agent – The rationale behind decisions
In creating digital experiences, the UX strategy harmonises the three dimensions mentioned above: business, users, and deployment. Not only does it unite these dimensions, but it intersects them, creating cohesion with clarity and objectivity.
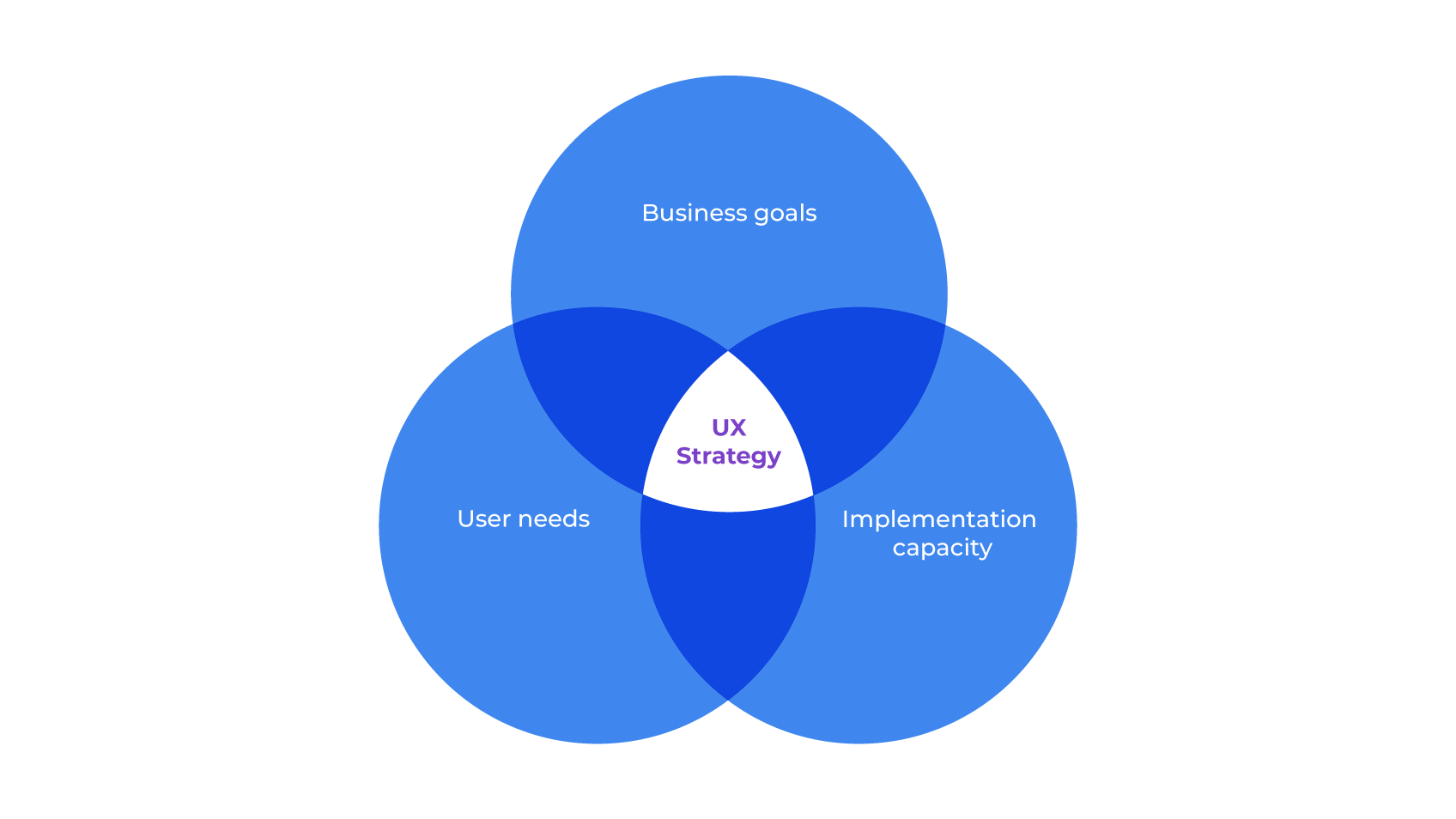
The space between these three dimensions is often fertile ground for misunderstandings and wrong decisions. The strategy works to remove these gaps, reducing ambiguity.
By eliminating guesswork, the strategy provides a solid basis for informed decisions – it is not based on hunches or intuition but on in-depth analysis and holistic understanding.
Every step of the experience creation process is carefully outlined by the UX strategy. From initial conception to implementation, each decision is supported by a clear rationale, underpinned by data, research and alignment, offering not just a functional product but an experience that fulfils or transcends expectations.
The UX strategy is a map that guides project teams through a complex terrain. Clearly define what must be done and, just as importantly, what must not be done, keeping the focus on the expected result.
4 – How we materialise a UX strategy at Xpand IT
How do we effectively implement this process in a company? The delivery resulting from the process can vary in terms of effort, depending on the depth and complexity of the challenges we face. From a one-day deadline to continuous presence, the process is flexible and adaptable to any situation.
UX Strategy in a day
- Discovery session to define the problem;
- Simple market analysis;
- Identify improvement opportunities;
- Presentation Pitch.
UX Strategy sprint
- Discovery session to define the problem;
- Research: Market analysis, competition, and digital approach (simple);
- Target identification and analysis (simple);
- Presentation of strategic value propositions;
- Concept creation: wireframe;
- Presentation and delivery of POC – proof of concept.
UX Strategy report
- Discovery and ideation session;
- Research: Market analysis, competition, and digital approach (extended);
- Identifying and analysing the target (creating personas);
- Presentation of strategic value propositions;
- Concept creation – UI;
- Presentation and delivery of POC – proof of concept;
- Results report identifying value propositions.
Continuous – UX as a Service
- Alignment with functional analysis team;
- Continuous allocation to the project;
- Active participation in several of the client’s strategic initiatives;
- Identifying new As a Service trends;
- Alignment of opportunities and long-term concept.
5 – Conclusion – UX strategy as a framework for experience
The UX strategy, outlined in this context, is not just a methodology but a structuring agent for all the elements of a project.
By eliminating guesswork, each step in the UX process is a conscious expression of strategy, where teams work collaboratively to create a cohesive narrative.
The success of a digital product is determined not only by its technical functionality but also by its overall experience. The UX strategy emerges as the guiding force behind this experience.
Finally, it is crucial to recognise that UX strategy is not static; it is dynamic and adaptable. As user needs evolve and business objectives adjust, the strategy is a flexible guide, ensuring that the digital experience remains aligned with the business’s vision.
Therefore, by incorporating a strategic mindset into the UX approach, we are not just creating digital products: we are forging experiences that transcend expectations, leaving a lasting mark on those who use and feel the digital product.